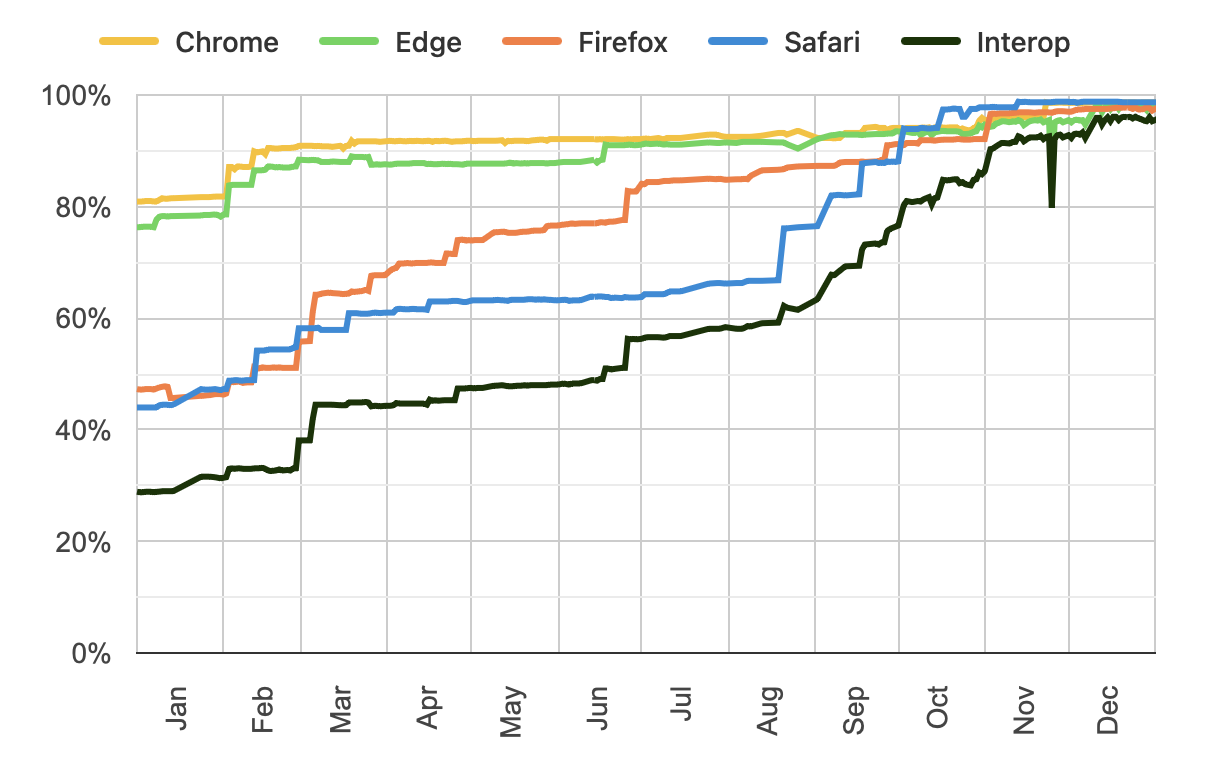
Exciting news for web developers, designers, and browser enthusiasts alike — Interop 2026 is here, continuing the mission of improving cross-browser interoperability. For the fifth year in a row, we are pleased to collaborate with Google, Igalia, Microsoft, and Mozilla to make web technology more consistent and reliable across our browsers.
Introducing Interop 2026
Making your website work in every browser can be a challenge, especially if browser engines have implemented the same web technology in slightly different ways. The Interop Project tackles this challenge by bringing the major browser engines together to improve the same set of features during the same year. Each feature is judged on whether or not it fully aligns with its official web standard — the formal technical specifications that define how each web technology should work. This helps accelerate progress toward a more reliable, consistent platform to build on.
Safari has already implemented many of the features included in Interop 2026. In fact, we were the first browser to ship contrast-color(), Media pseudo-classes, shape(), and Scoped Custom Element Registries. Plus, we have support for Anchor Positioning, Style Queries, Custom Highlights, Scroll Snap, View Transitions and much more. We’re excited that these technologies are being included as focus areas in Interop 2026, ensuring they get implemented across all browsers and any remaining interoperability gaps are closed.
We will also be focused on adding support for the following features: advanced attr(), the getAllRecords() method for IndexedDB, WebTransport, and the JavaScript Promise Integration API for Wasm. Together, these four areas make up 20% of the Interop 2026 score. They are exciting new features that solve real needs.
Focus Areas for 2026
The Interop Project measures interoperability through Web Platform Tests — automated tests that check whether browsers conform to web standards. Interop 2026 is ambitious, covering twenty focus areas. Fifteen are brand new. And five are carryovers from Interop 2025.
Anchor positioning
Anchor positioning is a carryover from Interop 2025, where significant progress was made to empower developers to position elements relative to each other. This year’s focus will be on clarifying the spec, resolving test issues, and increasing the reliability of this powerful layout feature.
Advanced attr()
The CSS attr() function lets you bridge the gap between structural data and visual presentation by pulling values directly from HTML attributes into your CSS, making styles more dynamic and context-aware without the overhead of JavaScript. While attr() has long been supported for the content property, advanced attr() extends it to work across all CSS properties with type conversion — letting you use HTML attribute values as colors, lengths, angles, and other data types. Now that security concerns have been worked through in the specification, browser makers are united in our excitement to ship this long-awaited capability with strong interoperability.
Container style queries
Style queries let you apply styles conditionally, based on the value of a custom property (aka, variable) as defined at a certain container. Similar to how Container size queries let your CSS respond to the size of the container, style queries let it respond to theme values, state flags, and other contextual data.
@container style(--theme: dark) {
.card {
background: #1a1a1a;
color: #ffffff;
}
}
Style queries started shipping in recent years, including in Safari 18.0. Interop 2026 will help ensure this powerful tool works consistently everywhere.
contrast-color()
The contrast-color() function in CSS returns a color — either black or white. It puts the burden on the browser to choose whichever has higher contrast with the color specified in the function.
.button {
background: var(--brand-color);
color: contrast-color(var(--brand-color));
}
By having the browser make the choice, you can architect your design system in a simpler fashion. You don’t need to manually define every color pairing. Safari and Firefox both shipped support in 2025, and now Interop 2026 will ensure this powerful function works consistently across all browsers.
Note, contrast-color() does not magically solve all accessibility concerns. Read about all the details in How to have the browser pick a contrasting color in CSS.
CSS Zoom
The CSS zoom property scales an element and its contents, affecting layout and making the element take up more (or less) space. Unlike transform: scale(), which is purely visual, zoom changes how the element participates in layout.
.card {
zoom: 1.5;
}
While zoom was supported in browsers for years as a non-standard property, it’s been plagued by inconsistencies in edge cases and how it interacts with other layout features. Now that it’s standardized, CSS zoom returns as a focus area in Interop 2026, continuing from 2025.
Custom Highlights
The CSS Custom Highlight API lets you style arbitrary text ranges without adding extra elements to the DOM. Using JavaScript, you create a highlight range, then style it with the pseudo-elements.
The ::highlight() pseudo-element is perfect for highlighting in-page search results, customizing syntax highlighting in code editors, creating an app that allows collaborative editing with user cursors, or any situation where you need to visually mark text without changing the document structure. The ::target-text pseudo-element styles the text that’s scrolled to when a user taps a link with a text fragment.
With implementations progressing across browsers, Interop 2026 ensures these highlighting capabilities work consistently, giving you reliable tools for text-based interactions.
Dialog and popover additions
The <dialog> element and popover attribute have transformed how developers build overlays on the web. Dialog was part of Interop 2022 and Popover was in Interop 2024. This year, three recent enhancements to these features make up this focus area for Interop 2026.
The closedby attribute lets you control how users can dismiss dialogs:
<dialog closedby="any">
</dialog>
The popover="hint" attribute creates subordinate popovers that don’t dismiss other auto popovers — perfect for tooltips:
<div popover="hint" id="tooltip">
This tooltip won’t close the menu!
</div>
The :open pseudo-class matches elements with open states, working with <dialog>, <details>, and <select>:
dialog:open {
animation: slideIn 0.3s;
}
Together, these additions make building accessible, user-friendly UI overlays easier than ever.
Fetch uploads and ranges
The fetch() method is getting three new powerful capabilities for handling uploads and partial content.
ReadableStream request bodies enable true streaming uploads, letting you upload large files or real-time data without loading everything into memory first:
await fetch('/upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: readableStream,
duplex: 'half'
});
Enhanced FormData support improves multipart uploads and responses.
Range header support allows partial content requests, essential for video streaming and resumable downloads:
fetch('/video.mp4', {
headers: { 'Range': 'bytes=0-1023' }
});
These enhancements bring fetch() up to par with more specialized APIs, reducing the need for custom solutions.
getAllRecords() for IndexedDB
IndexedDB is a low-level API that lets you store large amounts of structured data in the browser, including files and blobs. It’s been supported in browsers for many years.
Now, IndexedDB is getting a significant performance boost with the new getAllRecords() methods for IDBObjectStore and IDBIndex. These methods allow you to retrieve records in batches and in reverse order:
const records = await objectStore.getAllRecords({
query: IDBKeyRange.bound('A', 'M'),
count: 100,
direction: 'prev'
});
It’s just this new method that’s being included in Interop 2026. The score only reports the percentage of getAllRecords() tests that are passing — not all IndexDB tests.
JSPI for Wasm
WebAssembly has opened the door for running high-performance applications in the browser — games, productivity tools, scientific simulations, and more. But there’s been a fundamental mismatch. Many of these applications were originally written for environments where operations like file I/O or network requests are synchronous (blocking), while the web is fundamentally asynchronous.
The JavaScript Promise Integration API (JSPI) bridges this gap. It lets WebAssembly code that expects synchronous operations work smoothly with JavaScript’s Promise-based async APIs, without requiring you to rewrite the entire application. This means you can port existing C, C++, or Rust applications to the web more easily, unlocking a wider range of software that can run in the browser.
Interop 2026 will ensure JSPI works consistently across browsers, making WebAssembly a more viable platform for complex applications.
Media pseudo-classes
We’ve proposed media pseudo-classes for inclusion in the Interop Project for many years in a row. We are excited that it’s being included this year!
Seven CSS pseudo-classes let you apply CSS based on the playback state of <audio> and <video> elements:
These all shipped in Safari many years ago, but without support in any other browser, most developers don’t use them — or even know they exist. Instead developers need JavaScript to sync UI state with media playback state.
It’s far simpler and more efficient to use media state pseudo-classes in CSS.
video:buffering::after {
content: "Loading...";
}
audio:muted {
opacity: 0.5;
}
They are especially powerful combined with :has(), since it unlocks the ability to style anything on the page based on playback state, not just elements that are descendants of the media player.
article:has(video:playing) {
background-color: var(--backgroundColor);
color: contrast-color(var(--backgroundColor));
transition: background-color 0.5s ease;
}
Learn more about the power of :has() in Using :has() as a CSS Parent Selector and much more.
Navigation API
If you’ve built single-page applications, you may have experienced the pain of managing navigation state with history.pushState() and popstate events. Navigation API gives you a cleaner, more powerful way to intercept and control navigation.
This focus area is a continuation of Interop 2025, where significant progress was made to empower developers to initiate, intercept, and modify browser navigation actions. This year continues work on interoperability, to get the overall score up from the 92.3% test pass result during Interop 2025. Plus, there’s one new feature being added — the precommitHandler option. It lets you defer navigation until critical resources are ready, preventing jarring flashes of incomplete content.
navigation.addEventListener('navigate', (e) => {
e.intercept({
async precommitHandler() {
await loadCriticalData();
},
async handler() {
renderPage();
}
});
});
Interop 2026 will ensure Navigation API works reliably across browsers, a solid foundation for web applications.
Scoped custom element registries
Working with web components, you may have run into a frustrating limitation: the global customElements registry only allows one definition per tag name across your entire application. When two different libraries both define a <my-button> component, they conflict.
The CustomElementRegistry() constructor solves this by letting you create scoped registries. Different parts of your application — or different shadow roots — can have their own definitions for the same tag name.
const registry = new CustomElementRegistry();
registry.define('my-button', MyButtonV2);
shadowRoot.registry = registry;
This is especially valuable for microfrontends, component libraries, and any situation where you’re integrating third-party web components.
Safari 26.0 was the first browser to ship Scoped custom element registries. Inclusion in Interop 2026 will help ensure this capability works consistently across all browsers.
Scroll-driven Animations
Scroll-driven animations let you more easily create animations that respond to scroll position, now entirely in CSS. As a user scrolls, the animation progresses — no JavaScript needed. You can build scroll-triggered reveals, progress indicators, parallax effects, and interactive storytelling experiences.
Define animations with standard CSS keyframes, then connect them to scroll using animation-timeline:
.reveal {
animation: fade-in linear forwards;
animation-timeline: view();
animation-range: entry 0% entry 100%;
}
@keyframes fade-in {
from { opacity: 0; }
to { opacity: 1; }
}
Use view() to trigger animations as elements enter and exit the viewport, or scroll() to tie animations to a scrolling container’s position. Learn much more in A guide to Scroll-driven Animations with just CSS.
We shipped support for scroll-driven animations in Safari 26.0. Interop 2026 will help ensure this feature works consistently across all browsers.
Scroll Snap
CSS Scroll Snap controls the panning and scrolling behavior within a scroll container, creating carousel-like experiences:
.carousel {
scroll-snap-type: x mandatory;
overflow-x: scroll;
}
.carousel > * {
scroll-snap-align: center;
}
Scroll Snap has been supported in all modern browsers for many years. But like many of the older CSS specifications, multiple rounds of changes to the specification while early versions were already shipping in browsers created a deep lack of interoperability. With a far more mature web standard, it’s time to circle back and improve interoperability. This is the power of the Interop Project — focusing all the browser teams on a particular feature, and using automated tests to find inconsistencies and disagreements.
shape()
For years, when you wanted to create a complex clipping path to use with clip-path or shape-outside you’ve been limited to polygon(), which only supports straight lines, or SVG paths, which aren’t responsive to element size changes.
Now, the shape() function lets you create complex shapes with path-like commands (move, line, curve). It gives you the best of both worlds — curves like SVG paths, but with percentage-based coordinates that adapt as elements resize.
.element {
clip-path: shape(
from 0% 0%,
line to 100% 0%,
line to 100% 100%,
curve to 0% 100% via 50% 150%,
close
);
}
We shipped support for the shape() function in Safari 18.4. And we look forward to Interop 2026 improving browser implementations so you can confidently use it to render of complex, responsive curves.
View transitions
View Transitions was a focus area in Interop 2025, narrowly defined to include same-document view transitions and view-transition-class. These features allow for smooth, animated transitions between UI states within a single page, as well as flexible control over styling those transitions.
While Safari finished Interop 2025 with a score of 99.2% for view transitions, the overall interoperability score is at 90.8% — so the group decided to continue the effort, carrying over the tests from 2025.
For Interop 2026, the focus area expands to also include cross-document view transitions. This allows you to create smooth, animated transitions in the moments between pages as users navigate your site, rather than an abrupt jump when new page loads. Cross-document view transitions shipped in Safari 18.2. Learn more about it in Two lines of Cross-Document View Transitions code you can use on every website today.
Web Compat
Web compatibility refers to whether or not a real world website works correctly in a particular browser. When a site works in one browser, but not another — that’s a “compat” problem. This focus area is made up of a small collection of Web Platform Tests selected because the fact they fail in some browsers causes real websites to not work in other browsers — thus creating problems for both web developers and users.
Each time Web Compat has been a focus area as part of the Interop Project, it’s targeted a different set of compat challenges. This year, Interop 2026’s web compatibility work includes:
WebRTC
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) enables real-time audio, video, and data communication directly between browsers, without requiring plugins or intermediate servers. You can build video conferencing apps, live streaming platforms, peer-to-peer file sharing, and collaborative tools.
Having reached a 91.6% pass rate, WebRTC continues as a focus area in 2026, building on the progress made during Interop 2025. We’re looking forward to fixing the long tail of interop issues of the main spec for WebRTC.
WebTransport
WebTransport provides a modern way to transmit data between client and server using the HTTP/3 protocol. It gives you low-latency bidirectional communication with multiple streams over a single connection. You get both unreliable datagram support (like UDP) for speed and reliable stream support (like TCP) for guaranteed delivery.
const transport = new WebTransport('https://example.com/endpoint');
await transport.ready;
const stream = await transport.createBidirectionalStream();
WebTransport is ideal for gaming, real-time collaboration tools, and applications where you need more control than WebSocket provides but don’t want to manage WebRTC’s complexity. Being part of Interop 2026 ensures WebTransport works consistently across all browsers, making it a reliable choice for real-time data transmission.
Investigation Efforts: A Look Ahead
In addition to the focus areas, the Interop Project includes four investigation areas. These are projects where teams gather to assess the current state of testing infrastructure and sort through issues that are blocking progress.
Accessibility testing
Continuing from previous years, the Accessibility Testing investigation aims to work towards generating consistent accessibility trees across browsers. This effort will improve the WPT testing infrastructure for accessibility on top of the foundation from Interop 2024. This work ensures that accessibility features are reliable and consistent, helping developers create more inclusive web experiences.
JPEG XL
JPEG XL is a next-generation raster graphics format that supports animation, alpha transparency, and lossy as well as lossless compression. We shipped support for it in Safari 17.0. This investigation will focus on making the feature properly testable by developing comprehensive test suites, opening up the possibility that JPEG XL could be a focus area in the future.
Mobile testing
The Mobile Testing investigation continues work started in 2025. This year, we will focus on improving infrastructure for mobile-specific features like dynamic viewport changes which are crucial for building responsive mobile web experience that billions of users rely on every day.
WebVTT
Continuing from 2025, the WebVTT investigation addresses a critical challenge facing the web platform. Developers cite WebVTT’s inconsistent behavior across browsers as a major reason for choosing other subtitling and captioning solutions. Our investment in WebVTT last year primarily consisted of validating and fixing the existing test suite, as well as making any necessary spec changes along the way. We are excited to continue that effort this year to ensure synchronized text tracks and closed captioning work seamlessly across the web.
A more interoperable web
Interop 2026 brings together twenty focus areas that matter to you as a web developer. Some, like attr() and contrast-color(), give you more flexible ways to architect your CSS. Others, like Scroll-Driven Animations and View Transitions, let you create smoother, more engaging experiences without reaching for JavaScript. Features like WebTransport and the Navigation API give you more powerful tools for building modern web applications.
Just as important are the focus areas working to fix long-standing inconsistencies — ensuring Scroll Snap works reliably, bringing all browsers up to speed on shape(), and solving real-world compatibility problems that have been frustrating developers and breaking sites.
The WebKit team is committed to making these features work consistently across all browsers. Whether you’re building a design system, a single-page application, a video streaming platform, or anything in between, Interop 2026 is working to give you a more reliable foundation to build on.
Here’s to another year of making the web better, together!





 ).
).